35.6.8 Comparators
������������Accuracies commonly below 1/10 thousandth of an inch
These instruments try to reduce the friction that is such a problem for the dial indicators
There are four common principles used to design these instruments,
comparators have very limited ranges of motion, but very high sensitivities (and therefore accuracies). As a result the comparators are often calibrated against standards such as gauge blocks.
The basic requirements of these instruments are,
35.6.8.1 - Mechanical Comparators
������������The Johansson Mikrokator used a twisted strip with a pointer attached. as the plunger is depressed, it causes the strip to stretch. As the twisted strip is stretched, it changes the angle of the pointer, and thus the indicated deflection.

The Sigma Mechanical Comparator uses a partially wrapped band wrapped about a driving drum to turn a pointer needle.

35.6.8.2 - Mechanical and Optical Comparators
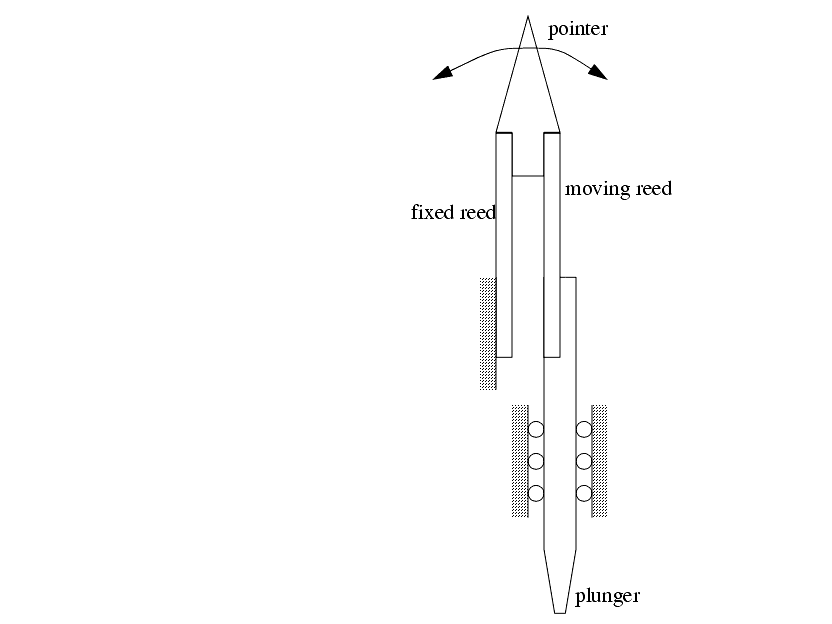
������������The Eden-Rolt Reed system uses a pointer attached to the end of two reeds. One reed is pushed by a plunger, while the other is fixed. As one reed moves relative to the other, the pointer that they are commonly attached to will deflect.
35.6.8.3 - Optical Comparators
������������These devices use a plunger to rotate a mirror. A light beam is reflected off that mirror, and simply by the virtue of distance, the small rotation of the mirror can be converted to a significant translation with little friction.
35.6.8.4 - Pneumatic Comparators
������������

The Soloflex Back Pressure System uses an orifice with the venturi effect to measure air flow. If the gas is not moving, the pressure on both sides of the orifice will be equal. If the flow is moving quickly, the air pressure on the downstream side of the orifice will be at a lower pressure.
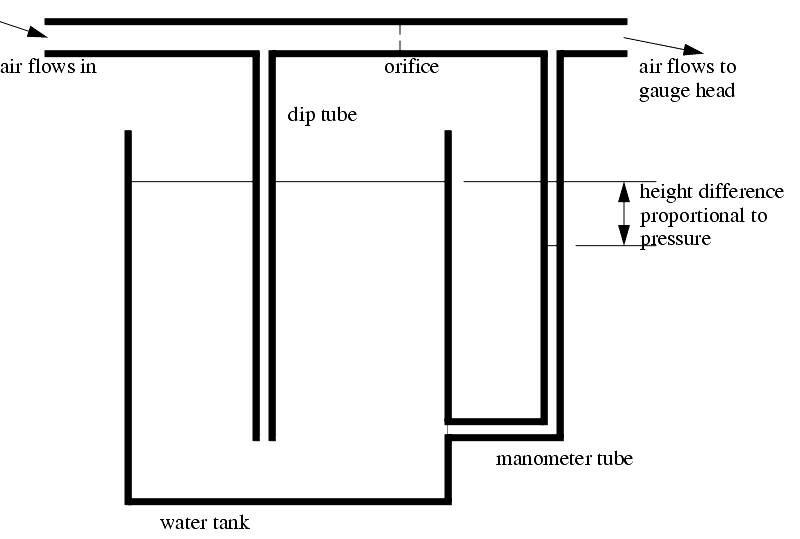
A Differential Back Pressure system uses a split flow channel, one flow goes to the gauge head, the other goes to a zero offset valve. A meter measures the difference in pressures, and thus gives the differences in pressure.
35.6.9 Autocollimators
������������35.6.10 Level Gauges
������������35.6.10.1 - Clinometer
������������35.6.10.2 - The Brookes Level Comparator
������������35.6.11 The Angle Dekkor
������������Measures surface flatness using collimated light, and a moving lens to focus the beam as it travels across the test surface.