4.12 Practice Problems
������������1. What would happen if a drill without flutes was used?
2. If we want a hole with a 1/2-14-UNC thread, what size of tap drill should be used?
3. What type of drill press is suitable for drilling holes in car engine blocks? Justify your answer.
4. Which of these statements is not correct?
5. Which of these statements is correct?
6. Which of the following statements is not correct?
7. Which of the following is not a typical drill press operation?
8. Which of the statements is most correct?
9. Given a hole that is to be drilled then reamed to 3.000", develop a process plan including speeds and feeds.
10. We want to drill a hole that is 2.369" in diameter. If we know that the accuracy the shop can provide for drilling is +0.030" to -0.010",
11. Calculate the machine tool spindle speeds for the following,
12. We are to drill 6 holes in a 2" thick mild steel plate. The plate is held in a jig. We are using a 63/64" high speed steel drill, and the suggested parameters are CS = 80 ft./min. with a feed of 0.004"/rev. After drilling each hole is to be finished with a 1.0" diameter reamer. If the suggested parameters for the reamer are CS = 80 ft./min. with a feed of 0.010"/rev.,
b) find the cost to produce 500 parts when each part needs 3 minutes for setup (no operation), labor rates are $25/hr., and overhead is $25/hr.
13. Which of these statements is not correct?
14. Which of these statements is correct?
15. Which of the following statements is not correct?
16. Which of the following is not a typical drill press operation?
17. Which of the statements is most correct?
18. What are functions of the following parts of a drill bit. a) body, b) web, c) point, d) tang, e) margin, f) flutes, g) body clearance.
19. What are the purposes of the following drill points. a) conventional, b) flat, c) long angle.
20. What applications are the following drill bits well suited to? a) high helix, b) straight flute, c) gun, d) hard steel, e) core, f) oil hole.
21. What will happen if a drill bit has unequal angles on the cutting edges/lips? What if the edges are not of equal length?
22. Why should most holes be started with a center drill?
23. What are the disadvantages of a thick web found on some drills?
24. What is the purpose of pilot holes?
25. What is the main difference between a) threading operations and tapping operations? b) boring and reaming?
26. List 5 ways work can be held in a lathe.
27. Can peripheral and face milling be done with the same cutter? How common is this?
28. Describe the steps in cutting a 3/8-12-UNC taped hole.
(ans. center drill, drill 1/4", drill .292", starting tap, finishing tap)
29. a) Explain the cutting mechanism of a drill bit, and b) suggest the features of a drill bit for cutting a thin piece of sheet metal.
1. A 2" diameter milling cutter with 8 teeth has been selected. What is the table feed if we are milling at 80 ft./min. with a tooth load of 0.004"/tooth?
2. Calculate the machine tool spindle speeds for the following,
b) milling with a 150mm diameter tungsten carbide tipped face cutter in stainless steel work. The CS is 65 m/min.
3. You are given a block of aluminum (5" by 5" by 5") and you must mill off a 1/16" layer. Using the tables for speeds and feeds, and using the other details provided below, determine a cost for the operation.
Milling cutter - high speed steel
- 10 teeth with a tooth load of 0.004" per tooth
- cost for the machine is $20.00 per hours

4. Which of the following statements is true for milling?
5. What are the advantages of upcut and downcut milling?

6. Which of the following statements is true for milling?
7. Given a 3" dia. 8 tooth fly cutter, with carbide cutting points, and a steel work piece, recommend, a) RPM, b) feed.
8. Given a 6" dia. high speed steel arbor mill with 10 teeth, that will be cutting cast iron work, recommend, a) RPM, feed.
9. Calculate the indexing required when would be cutting a gear with 36 teeth? Use one of the Brown and Sharp indexing plates.
10. Determine the angular indexing required (on Brown and Sharp, and Cincinatti Standard plates) if we want an angle of 23°30'.
1. Given that a tapered piece is to be made with the tailstock offset method, determine the taper per foot, and offset required if, you are starting with a bar of stock that is 8" long, and 1.125" in diameter, and the final taper is to be 6" long and 1" at the small end.
(ans. tpf = 0.25", offset = 0.0833")
2. Given the 1/2-12 UNC thread that is to be cut on the lathe,
a) What should the gear ratio between the machine spindle and the lead screw be if the lead screw is 5 t.p.i.?
3. Which of the following statements about lathe toolbits is correct?
4. Which of the statements about lathes below is most correct?
5. When turning between centres a dog is required; what is a dog in this context?
(ans. it holds the work piece so that it can be driven with a face plate mounted on the lathe spindle)
6. A centre gauge (fish tail gauge) is employed in thread cutting. Suggest two uses for the gauge.
(ans. aligning a cutting tool for threads, )
7. Given an external 9/16-12-UNC thread, determined which tools would be used.
(ans. a turning tool to turn the outside diameter of 9/16"+1/12", UNC tool to turn thread)
8. If we are rough cutting a 5" diameter bar of bronze on a lathe with a HSS tool,
c) if the setup time is 5 minutes, and the machine rate is $50/hr., what will the cost of the operation be?

9. List the basic steps for setting up a lathe to cut a thread on a bar of stock, assume the stock is mounted between centres already.
(ans. see thread cutting section)
10. If a taper of 1mm in 10mm is to be cut, what will the offset distance be for a 10cm part?
11. Calculate the machine tool spindle speeds for the following,
a) turning on a lathe with a high speed steel tool in mild steel work with a diameter of 2.75". The cutting speeds is 100 ft./min.
12. We have been given a mild steel bar that is to be turned on a lathe. It has a diameter of 14" and a length of 28". We have been asked to make two rough passes, and one finishing pass. The tool we have selected is Carbide. When doing rough cuts we use a feed of 0.007"/rev., and for finishing cuts we use a feed of 0.004"/rev. How long will this operation take?
13. Which of the following statements about lathe toolbits is correct?
14. Which of the statements about lathes below is most correct?
15. Given the non-standard 3/8-19 UNC thread that is to be cut on the lathe,
a) What should the gear ratio between the machine spindle and the lead screw be if the lead screw is 4 t.p.i.?
16. Develop a rough process plan for the part below by clearly listing operation steps in the correct sequence. Feeds, speeds, times and costs are not needed at this time.


17. The aluminum component below is to be turned on a lathe using a HSS tool. Develop a process plan, including offset for the taper, speeds, feeds, etc. Put the process plan in a list similar to the format shown. Assume a cost of $45.00/hr. for the lathe, and $25.00/hr. for all other pieces of equipment. State all assumption clearly, and justify numbers in the process plan with calculations or references.

18. On a lathe toolbit what are the functions of, a) the side relief angle, b) end relief angle, c) back rake, d) side rake angle, nose radius.
19. What applications are large positive rake angles for? negative rake angles?
20. What is the difference between end and face milling?
21. What RPM should be used to rough cut a cast iron piece with a 3" dia. with a high speed steel tool. What RPM should be used for a similar workpiece of plain carbon steel? What RPM should be used for the two materials if finishing cuts are being made?
22. Calculate the time required to machine a 2" dia. copper rod that is to be turned for a length of 10".
23. What are rough and finish turning operations used for?
24. What are two methods for cutting stepped shoulders on a lathe?
25. Explain the difference between self holding and steep tapers using the coefficient of friction.
26. Find the tpf and tailstock offset for tapers on the following work.
a) D=1.5", d=1.25", TL=4", OL=8"
27. convert a metric taper of 1:50 to a tpf. Convert a 1"tpf to metric.
28. Define the terms, fit, tolerance, allowance, limits, clearance, press fit, precision.
29. For a 1"-8-NC thread find the minimum and maximum diameters and minimum width of the toolbit point.
30. Describe the differences in speeds, feeds and depths of cuts for roughing and finishing cuts.
31. What types of chips are desirable when setting up automated cutting processes?
32. Compare the time to cut a work piece using a high speed steel tool and a carbide tool. The 4" dia. aluminum work is to be rough turned over a length of 14".
33. What operations can be performed on a lathe?
34. How are the parameters different for a lathe when turning, as opposed to finishing?
35. A taper is to be cut on the aluminum part below. Indicate how far the tailstock should be offset and the speed and feed settings for the lathe.

(ans. offset=0.4", feed 0.005-0.010", speed 760RPM)
1. An orthogonal cut is made with a carbide tool having a 15° positive rake angle. The various parameters were noted,
b) From the Merchant Circle diagram find the shear angle (f), friction force (F), friction normal force (N), and shear force (Fs).
(ans: F = 218lb., N = 330lb., f= 19.37°, Fs = 312 lb., m= 0.948, Vc = 250 ft./min., Vf = 83.5 ft./min. Q = 9.375 in3/min.)
2. The cutting forces for a lathe are listed below,
b) Find a maximum lathe horsepower, assuming the machine efficiency is 95% and it requires 1/8 idle horsepower.
3. What roles do rake and relief angles play in cutting tools?
ans. the rake angle will change the basic cutting parameters. A positive rake (sharp tool) will give lower cutting forces, but less edge strength. A negative or neutral rake will give higher cutting forces, but more strength. The relief angle provide a gap behind the cutting edge so that the tool does not rub the work.
4. Which of these statement is the most correct?
5. One of the assumptions behind orthogonal cutting is,
6. Which of these statements is correct?
c) we can use the quantity of metal removed by itself to estimate the required horsepower of a machine tool.
7. A lathe toolbit with a rake angle of 20° is cutting a section of pipe with an inner diameter of 6" and an outer diameter of 6.25". The cut has a depth of 0.010" and the chip has a thickness of 0.020". If the lathe is turning at 200 rpm, and the measured cutting forces are Fc = 300 lb, and Ft = 125lb,
b) find the following values using a graphical or numerical solution: (Marks are only awarded for correct answers) Fs, FN, F, N, t, f, m, Vc, Vf, Vs.

8. Calculate the machine tool spindle speeds for the following:
a) Milling with a tungsten carbide tipped face cutter on a stainless steel work piece. C.S. = 65 m/min., cutter dia. = 150mm.
b) Drilling with a High Speed Steel drill in Machine Steel work, with C.S. = 70 ft./min., and a drill diameter of 19/32"
c) Turning on a lathe with a High Speed Steel tool in a mild steel work piece. Surface cutting speed = 100 ft./min., and a workpiece diameter of 2.75"
d) Milling with a High Speed Steel cutter in tool steel work with a cutter speed of 60 ft./min., and a cutter diameter of 3/4".
a) Why are ceramics normally provided as inserts for tools, and not as entire tools?
b) List the important properties of cutting tool materials and explain why each is important.

10. A turning cut was made in a magnesium workpiece with a feed of 0.050ipr. The cutting speed was 300 fpm, and the cutting force was measured as 200lbs. The lathe is 95% efficient and has an idle horsepower of 0.1HP. Using all of the provided information estimate the horsepower required for the cut.

11. Develop an expression that is the ratio friction power over cutting power using the equations for orthogonal cutting power. Simplify the expression to be in terms of measured values (rake angle, Fc, Ft, and chip thicknesses).
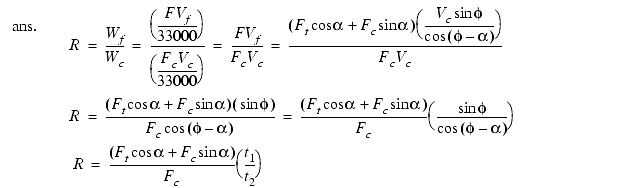
12. A new lathe tool is to be used on cast iron work with a 6" diameter to make a 5" long rough cut in 3 passes. The operation conditions listed below were provided by the supplier or assumed. Calculate the parameters a) to e) as requested.
13. Which of these statement is most correct?
14. One of the assumptions behind calculating orthogonal cutting forces is,
15. Which of these statements is most correct?
c) we can use the quantity of metal removed by itself to estimate the required horsepower of a machine tool.
16. A new lathe tool is to be used on cast iron work with a 6" diameter to make a 36" long rough cut in 4 passes. The operation conditions listed below were provided by the supplier or assumed. Calculate the parameters a) to e) as requested.
ans. a) 127rpm, b) 113min., c) 2.4 ipm, d) 1.23 or 3.94HP, e) 1.62 or 4.63HP

17. a) Define machinability. b) What determines the machinability of a metal?
20. What factors will affect surface finish?
21. Sketch a single edge cutting tool and label the a) face, b) flank, c) nose, d) cutting edge, e) relief, f) shank.
22. Why is the cutting speed important? What will happen at different cutting speeds, from very slow to very fast?
23. We have set up a lathe and are doing an orthogonal cut. The feed rate of the lathe is 0.1mm, and the chip thickness after the cut is 0.2mm. The depth of the chip being cut is 5mm. The surface cutting speed of the tool is 2m/s. The tool has a rake angle of 10deg. The tangential force is measured as 200N, and the cutting force is 500N. a) Calculate the shear force and velocity. b) Calculate the total energy produced in the cut, c) Calculate the energy used to shear d) Explain the difference between the total and the shear energy. [based on Kalpakjian]

24. How is machining different than other processes?
25. What is the difference between a roughing and finishing operation? How does this affect the workpiece and the power consumed?
26. What type of chip is expected at higher cutting speeds?
27. Does the friction power in cutting increase more with a feed or speed increase?
28. Why does cost typically increase for finishing operations.
29. Explain the correction factor `c' used with the HPu values.
(ans. the HPu values are not linear, and `c' corrects for these non-linear values)