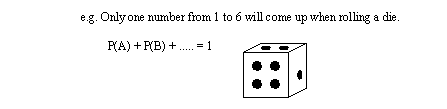
• A way to figure out how chances interact
• Mutually Exclusive - Probable events can only happen as one or the other.
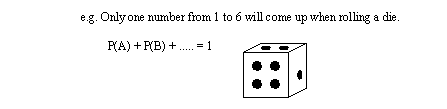
• Not Mutually Exclusive - Probable events can occur simultaneously
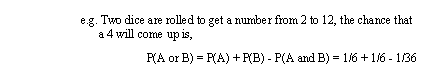
• Independent Probabilities - Events will happen separately
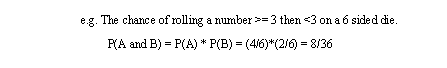
• Dependant Probabilities - The outcome of one event effects the outcome of another event

• Permutations - for exact definitions of not only possibilities, but also order.
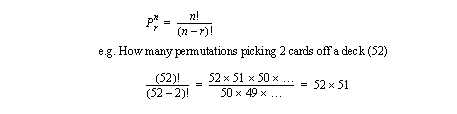
• Combinations - similar to before except order does not mater.
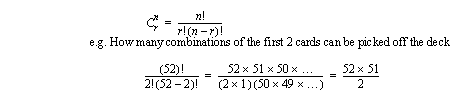
• empirical probability - experimentally determine the probability with,
