
|
|
|
10.3 GRINDING WHEELS
������������The wheels are typically made with a bonded abrasive.
Grain size is typically from 6 to 600.
The bonding mechanisms used commonly are,
The Grade of the wheel is a measure of the ability to retain grit. If a wheel is Grade A it is soft, if it is Grade Z, it is very hard.
The wheels are also given a structure number. 1 indicates a dense structure, whereas, 15 indicates an open structure.
Loading of a wheel refers to the embedding of swarf in the voids.
Glazing occurs when the grit has dulled, but is still bonded to the surface.
Grinding wheels should undergo a dressing process.
Many grinding wheels are shaped. This shaping is done while the wheel in the machine using diamond, or other hard shaping tools.
10.3.1 Operation Parameters
������������The wheel can be made to act soft by increasing work speed, and decreasing wheel speed. The wheel can be made to act hard by reversing the parameters.
Typical operation parameters are a depth per pass.
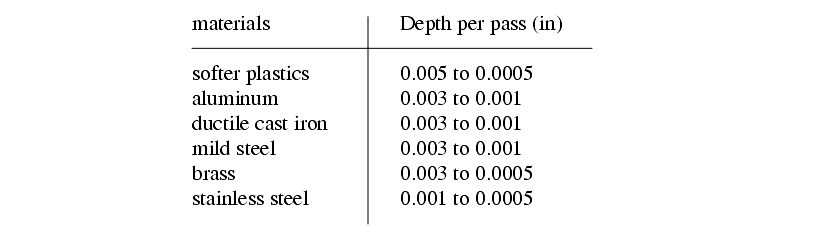
The wheel normally turns to give a CS of 3500 to 6000 fpm and wheels range from diameters of a few inches to a few feet.
The table feed is 80-350 fpm for finishing passes. Up to 1000 is reasonable.
Search for More: |

Custom Search
|

|