• This language allows tools to be programmed using geometrical shapes. This puts less burden on the programmer to do calculations in their heads.
• APT programs must be converted into low level programs, such as G-codes.
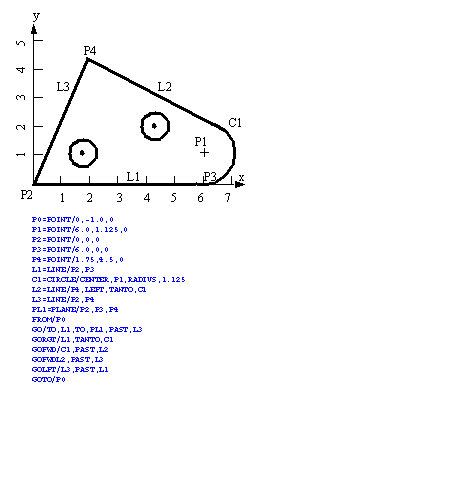
• An example of an APT program is given below.

• Some samples of the geometrical and motion commands follow. These are not complete, but are a reasonable subset.
• GEOMETRY: The simplest geometrical construction in APT is a point
p=POINT/x,y,z - a cartesian point
p=POINT/l1,l2 - intersection of two lines
p=POINT/c - the center of a circle
p=POINT/YLARGE,INTOF,l,c - the largest y intersection of a line and a circle
*Note: we can use YSMALL,XLARGE,XSMALL in place of YLARGE
• GEOMETRY: Lines are one of the next simplest definitions,
l=LINE/x1,y1,z1,x2,y2,z2 - endpoint cartesian components
l=LINE/p,PARLEL,l - a line through a point and parallel to another line
l=LINE/p,PERPTO,l - a line through a point and perpendicular to a line
l=LINE/p,LEFT,TANTO,c - a line from a point, to a left tangency point on a circle
l=LINE/p,RIGHT,TANTO,c - a line from a point, to a right tangency point on a circle
l=LINE/LEFT,TANTO,c1,LEFT,TANTO,c2 - defined by tangents to two circles
l=LINE/LEFT,TANTO,c1,RIGHT,TANTO,c2 - defined by tangents to two circles
l=LINE/RIGHT,TANTO,c1,LEFT,TANTO,c2 - defined by tangents to two circles
l=LINE/RIGHT,TANTO,c1,RIGHT,TANTO,c2 - defined by tangents to two circles
• GEOMETRY: Circles are very useful for constructing geometries
c=CIRCLE/x,y,z,r - a center and radius
c=CIRCLE/CENTER,p,RADIUS,r - a center point and a radius
c=CIRCLE/CENTER,p,TANTO,l - a center and a tangency to an outside line
c=CIRCLE/p1,p2,p3 - defined by three points on the circumference
c=CIRCLE/YLARGE,l1,YLARGE,l2,RADIUS,r - tangency to two lines and radius
*Note: we can use YSMALL,XLARGE,XSMALL in place of YLARGE
• GEOMETRY: More complex geometric constructions are possible
QUADRIC/a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j - define a polynomial using values
GCONIC/a,b,c,d,e,f - define a conic by equation coefficients
LCONIC/p1,p2,... - defines a conic by lofting (splining) points
RLDSRF/ - a ruled surface made of two splines
POLCON/ - define a surface using cross sections
PATERN/ - will repeat a motion in a linear or circular array
• Once we have constructed points, lines and circles we can then proceed to direct the tool to follow the path.
• MOTION: We can use the basic commands to follow the specified geometry
FROM/p - specify a start point
FROM/x,y,z - specify a start point
GOTO/p - move to a final point
GOTO/x,y,z - move to a final point
GOTO/TO,p - move until the tool touches a point
GOTO/TO,l - move until the tool touches a line
GOTO/TO,c - move until the tool touches a circle
GOLFT/l1,TO,l2 - go on the left of l1 until the tool touches l2
GORGT/l1,TO,l2 - go on the right of l1 until the tool touches l2
GOBACK/l1,TO,l2 - reverses direction along l1 to l2
GOBACK/l1,TO,c1 - reverses direction along l1 to c1
GOUP/l1,TO,l2 - goes up along l1 to l2
GODOWN/1l,TO,l2 - goes down along l1 to l2
GODLTA/x,y,z - does a relative move
Note: TO can be replaced with PAST, ON to change whether the tool goes past the structure, or the center stops on the structure.
• MOTION: The following commands will create complex motion of the tool
PSIS/ - will call for the part surface
• As would be expected, we need to be able to issue commands to control the machine.
• CONTROL: The following instructions will control the machine outside the expected cutting tool motion.
CUTTER/n1,n2 - defines diameter n1 and radius n2 of cutter
MACHIN/n,m - uses a post processor for machine ‘n’, and version ‘m’
COOL/ANT/n - either MIST, FLOOD or OFF
TURRET/n - sets tool turret to new position
TOLER/n - sets a tolerance band for cutting
SPINDL/n,CW - specifies n rpm and direction of spindle
• We can also include some program elements that are only used for programming
• PROGRAM: The following statements are programming support instructions
REMARK - starts a comment line that is not interpreted
$$ - also allows comments, but after other statements
NOPOST - turns off the post processor that would generate cutter paths
CLPRNT - prints a sequential history of the cutter center location
SQRTF(n) - calculates the floating point square root
PARTNO/n - allows the user to specify the part name
LOOPST and LOOPND - loop instructions
RESERV/n,m - defines an array of size ‘n’ by ‘m’
JUMPTO/n - jump to line number
• Note: variables can also be defined and basic mathematical operations can be performed.